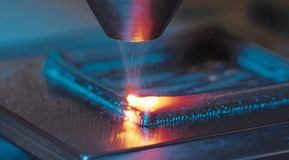

Process gases are used for laser welding and surface treatment. Welding gases protect the melt pool from reacting with the surrounding air.
Gases for CO2 laser welding
Controlling the formation of plasma is an important aspect of laser welding with high power CO2 lasers. Helium and helium/argon mixtures are typically used in laser welding with CO2 lasers. Since helium suppresses the formation of plasma, it is often used in high power laser welding. Since argon generates a large amount of plasma, it should not be used alongside high CO2 laser outputs.
For certain applications, mixtures of helium/argon with oxygen, carbon dioxide and other additives may be used. In laser welding is LASGON®, a specially developed program, with tailor-made gas mixtures for different laser welding applications, presents an alternative to helium.
Argon/hydrogen mixtures provide high productivity and weld quality when welding austenitic stainless steel.
When laser welding with an Nd:YAG laser, argon is recommended as a welding gas. Helium is rarely used, since plasma formation is not critical to Nd:YAG laser welding with normal laser outputs. From a quality perspective, argon often provides a better result than helium.
In principle, the same gases are used as in laser welding. Noble gases, i.e. argon and helium, protect the treated material from reacting with the surrounding atmosphere. In certain cases, nitrogen may be used as a process gas, depending on the type of material and additive. Argon/nitrogen mixtures are also used for certain applications.


